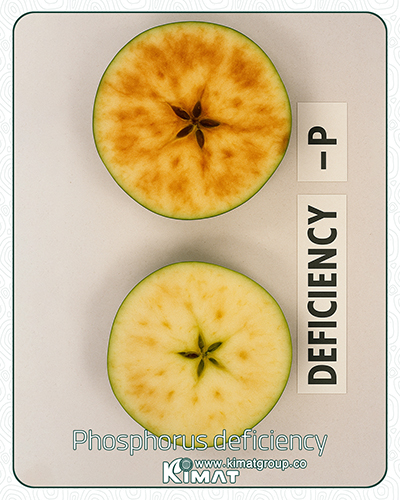
Phosphorus deficiency in plants
Key roles of phosphorus in plants:
✅ Early growth and maturity: Phosphorus promotes uniformity and accelerates plant maturity by stimulating early root growth.
✅ Increased stress resistance: Phosphorus increases the plant’s tolerance to cold, drought, and environmental stresses by optimizing water and element consumption.
✅ Reproductive efficiency: The presence of sufficient phosphorus improves flower and seed formation and enhances reproductive efficiency.
✅ Strengthening roots and stems: Phosphorus is essential for strong root establishment, optimal vegetative growth, and improved seed and fruit quality.
✅ Role in energy transfer: Phosphorus plays a key role in energy transfer, cell division, and the synthesis of vital plant compounds.
Some symptoms of phosphorus deficiency in plants:
- The plant remains smaller and shorter than normal.
- Older leaves turn an unnatural dark green color.
- Flower, fruit, and seed formation are reduced.
- Product late arrival
- Branches become thin on fruit trees.
Causes of phosphorus deficiency in plants:
- Improper soil pH: Phosphorus is best absorbed at pH 6 to 7.
- Cold soil temperatures: Decreased phosphorus uptake in early spring.
- Soil compaction: prevents root expansion and phosphorus absorption.
- Elemental competition: Too much iron, zinc, or calcium reduces phosphorus absorption.
- Weak roots: Surface or damaged roots are unable to absorb phosphorus.
Phosphorus management in plants:
- Reducing the pH of alkaline soils
- Increasing soil organic matter
- Irrigation management
- Using biological agents such as phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria in the soil
- Using appropriate sources of phosphorus fertilizer such as urea phosphate, monopotassium phosphate, monoammonium phosphate throughout the season in installments.